KNMFi Insights
sprungmarken_marker_1126
A Brief History Of KNMFi
Karlsruhe Nano Micro Facility (KNMFi) was founded in 2008 as an open access technology platform/research infrastructure for structuring and characterizing of functional materials at the micro- and nanoscale. In 2021, the scope of KNMFi was widened with the addition of digitalization and research data management. Operating with a collaborative approach to user access, KNMFi is currently organized in three laboratories hosting 23 technologies.
KNMFi is open to users from KIT, Helmholtz Centers as well as to worldwide users from industry and academia. Access is free of charge as long as results are intended to be published and are co-authored by KNMFi members or the resulting publication includes an acknowledgement to KNMFi. Registered users can apply to access KNMFi technologies via the KNMFi online proposal submission system.
Highlights
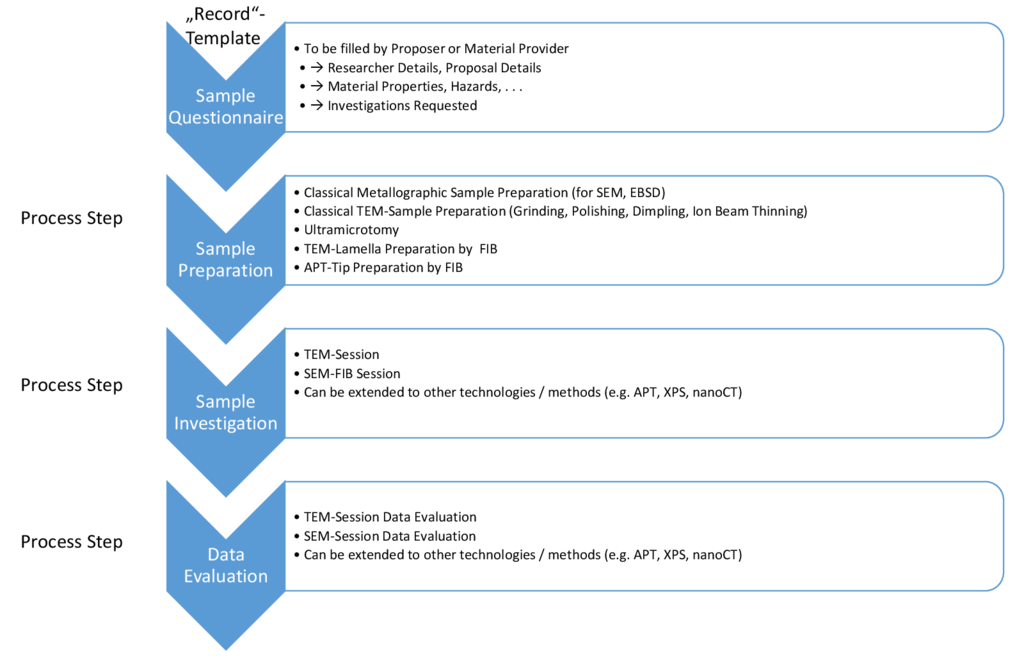
Karlsruhe, October 30, 2024 – A team of technology experts at the KNMFi user facility has published a practice paper (DOI: 10.5334/dsj-2024-050) detailing their approach to implementing the web-based application Kadi4Mat (KadiWeb) as an electronic laboratory notebook (ELN). The ELN is combined with an integrated MaTeLiS instrument database to support the principles of Findable - Accessible - Interoperable - Reusable (FAIR) research data.
Facing challenges in transmission electron microscopy (TEM), focused ion beam (FIB), atom probe tomography (APT), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), the team developed a strategy to document the complex processes in the KNMFi user facility. The experimental steps in TEM, APT, and FIB/SEM, as well as traditional sample preparation steps in a metallographic lab, were analyzed and translated into key-value pairs to create the respective templates. This is easily achievable without programming knowledge.
The MaTeLiS instrument database in Kadi4Mat enables users to find instruments at KIT and link them to experiments. In a practical example, the team demonstrated how the developed Kadi4Mat templates can be used to document experimental procedures in the TEM, APT, and FIB environments and how the MaTeLiS instrument database is integrated into Kadi4Mat. Experimental data can easily be added to the records, enabling FAIR data publication. The strategy can be extended to other KNMFi technologies.
Read more
May 5, 2024
Using the new NAPXAS instrument at the Karlsruhe Research Accelerator (KARA), researchers at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and the University of Münster aim to observe at the molecular level exactly how batteries charge and discharge. By making liquids accessible for synchrotron research with soft X-rays, NAPXAS provides unique insights into the processes at work in batteries.
NAPXAS (Near Ambient Pressure X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy) has been implemented at IQMT’s soft X-ray analytics facility WERA at the Karlsruhe Research Accelerator’s (KARA’s) KIT Light Source. “With NAPXAS, we can perform spectroscopic investigations of energy conversion and aging processes in batteries under more or less standard wet chemistry conditions, and we can do that live while the batteries are in use,” says Nagel, who is heading KIT’s work on the project.
After a test phase, plans call for researchers worldwide to have access to NAPXAS and WERA through the Karlsruhe Nano Micro Facility, a high-tech platform for research on functional materials in the micro- and nanometer range.
Press Release 039/2024